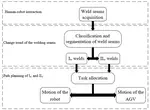
In the manufacturing process of cranes, a large number of shell and structural parts are connected by the welding process. The efficiency and accuracy of the welding process directly affect the advanced nature and productivity performance of manufacturing. The use of robots in the welding process is a development trend. At present, most of the robotic welding systems are fixed welding robot workstations and welding robots carried by gantries. In the process of crane manufacturing, workpieces have various types and some of them are large-scale, which causes thermal deformation in the welding process. At the same time, programming for welding robots is complex, and the skill requirements for operators are high. In order to improve welding accuracy and efficiency, this dissertation proposes a mobile welding system based on a collaborative robot. This dissertation studies the human-machine collaborative weld positioning method, mobile collaborative robotic welding process, and real-time seam tracking method based on line laser vision to simplify the welding process, reduce the skill requirements for operators, and achieve the continuous welding of large-size workpieces. The prototype of the equipment is built to verify the above key methods. The main research contents are summarized as follows: Firstly, this dissertation investigates the research and development in mobile welding technology, welding process based on human-machine collaborative, automatic welding equipment and seam tracking method in the domestic and overseas, analyzes the problems and requirements of the welding process in crane manufacturing, and proposes a mobile welding system based on a collaborative robot. The mechanical structure design, control system and software design are carried out. Combined with the overall design and requirements of the welding process, the key technologies of the mobile collaborative robotic welding system are refined. Secondly, in order to reduce the error between the actual seam position and the position in the three-dimensional model of the workpiece, a man-machine collaborative welding seam positioning method is proposed. The method of dragging teaching collaborative robot is used to quickly and conveniently locate the weld position of the workpiece. The vision-guided precise positioning based on image processing is used to accurately detect and locate the weld position. By analyzing the characteristics of the line laser at the weld position in the image, a method for the position of the torch and posture detection adjustment based on image processing is proposed. Then, due to the diversity of workpieces in the welding process, two kinds of collaborative welding modes are proposed: mobile platform fixed welding mode and collaborative mobile welding mode, by analyzing the motion characteristics of the mobile platform subsystem and welding robot subsystem, the task allocation method of welding process is proposed. Combined with the welding process characteristics, the weld tracking sensor is designed, and the installation position of the line laser transmitter and the camera is determined. The error sources in the welding process are analyzed and the error detection method is proposed. The real-time seam tracking algorithm is designed. Finally, a prototype of a mobile welding system based on a collaborative robot is built. The weld positioning experiment, mobile robot cooperative welding experiment and real-time weld tracking experiment are carried out. The feasibility of the above key methods is verified by a large number of experiments. The test data verify the efficiency and reliability of the proposed system.